How Early Childhood Education Shapes Future Success sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset.
Early childhood education plays a crucial role in shaping a child’s development and future achievements. By providing foundational skills in cognitive, social, and emotional areas, early learning experiences can significantly impact academic success later in life. With a focus on the importance of play, parental involvement, and diverse learning environments, this discussion will explore how these elements contribute to a child’s overall growth and the long-term benefits of investing in early education.
The Importance of Early Childhood Education
Early childhood education (ECE) serves as the cornerstone of a child’s developmental journey, laying the groundwork for their social, emotional, and cognitive growth. It encompasses a variety of programs and activities designed for children from birth to around eight years of age, a crucial period in their lives. The experiences children have during these formative years can significantly shape their future, influencing their approach to learning, relationships, and overall success.Research has consistently shown that high-quality early childhood education contributes to improved academic performance and lifelong benefits.
Engaging in structured learning environments helps children develop essential skills such as critical thinking, communication, and collaboration. These foundational skills establish a pathway for success in primary and secondary education, and ultimately in adulthood.
Foundational Role in Child Development
The role of early childhood education in child development cannot be overstated. During these early years, children’s brains undergo rapid growth and development. Quality ECE programs foster this growth by creating stimulating environments that promote exploration and creativity. Key milestones that significantly influence future achievements include:
- Language Development: Early exposure to language through reading and conversation enhances vocabulary and communication skills, which are critical for academic success.
- Social Skills: Interaction with peers in a structured setting teaches children how to share, cooperate, and resolve conflicts, essential skills for later teamwork and relationships.
- Emotional Regulation: Learning to express and manage feelings in a guided environment builds emotional intelligence, which is pivotal for personal and professional relationships.
- Cognitive Skills: Engaging in problem-solving activities promotes critical thinking and analytical skills that children carry into higher education and their careers.
Each of these milestones represents a building block upon which future learning and success are built. Investing in early childhood education is not just about immediate academic gains; it reflects a long-term commitment to shaping future generations capable of achieving their fullest potential.
“Quality early childhood education is the bedrock upon which future learning, social skills, and emotional health are built.”
The importance of early childhood education extends beyond academic readiness; it shapes the holistic development of children, equipping them with the necessary tools to navigate their future successfully. By providing enriching experiences during these formative years, we set the stage for lifelong learning and achievement.
Cognitive Development in Early Years: How Early Childhood Education Shapes Future Success
Early childhood education serves as a pivotal foundation for cognitive development, equipping young learners with essential skills that influence their future learning and overall success. The cognitive skills fostered during these formative years are crucial for problem-solving, critical thinking, and effective communication, all of which play significant roles in a child’s academic journey and personal growth.During early education programs, children engage in activities that stimulate their cognitive abilities.
These programs focus on enhancing various cognitive skills, such as memory, attention, and language development. For instance, when children participate in storytelling sessions, they not only improve their vocabulary but also learn to sequence events, which is fundamental in developing logical thinking. Moreover, hands-on activities encourage exploration and experimentation, allowing children to make connections and draw conclusions based on their observations.
Cognitive Skills Fostering Methods
Implementing specific methods can significantly enhance critical thinking and problem-solving skills in early childhood. These strategies create an environment where children feel safe to explore ideas and express solutions.One effective method is the use of open-ended questions during discussions and activities. Rather than asking yes/no questions, educators can pose questions that require children to think deeply and articulate their reasoning.
For example, instead of asking if a character in a story is happy, a teacher might ask what made that character feel that way, prompting children to analyze emotions and motivations.Additionally, incorporating play-based learning is highly beneficial. Play allows children to experiment with different roles, solve problems in real-time, and collaborate with peers. This not only develops their cognitive skills but also teaches important social skills.Here are some activities designed to promote cognitive growth:
- Building Blocks: Engaging with blocks fosters spatial awareness and problem-solving as children figure out how to balance structures.
- Puzzles: Completing puzzles enhances memory, pattern recognition, and critical thinking as children strategize how to fit pieces together.
- Science Experiments: Simple experiments, like mixing baking soda and vinegar, encourage inquiry and help children understand cause and effect.
- Role-Playing Games: Acting out different scenarios allows children to think creatively and develop narrative skills while enhancing social interaction.
- Storytelling and Story Mapping: Creating stories together encourages imagination, sequencing skills, and understanding narrative structure.
Engaging children in these activities not only nurtures their cognitive abilities but also instills a love for learning that can last a lifetime. By fostering an environment rich in exploration and curiosity, early childhood education significantly contributes to shaping capable problem solvers and critical thinkers for the future.
Social and Emotional Learning
Early childhood education plays a pivotal role in shaping social and emotional learning, which in turn lays the groundwork for future success. During these formative years, children learn to navigate their emotions, understand social cues, and develop relationships that are crucial for their overall development. This aspect of early education fosters resilience, empathy, and the ability to cope with challenges, which are essential traits for thriving in both academic and personal spheres.
Social skills and emotional resilience are significantly influenced by the experiences children have in early childhood education settings. Interactions with peers and educators provide opportunities for children to practice communication, share, negotiate, and resolve conflicts. These experiences not only enhance their social competency but also contribute to emotional growth. Children who engage in regular social interactions are more likely to develop strong communication skills, which are vital for expressing needs, feelings, and ideas effectively.
Peer Interactions and Communication Skills
Peer interactions in early childhood education are crucial for developing effective communication skills. Children learn best through play and structured group activities, where they are encouraged to express themselves and collaborate with others. This environment fosters the following essential skills:
- Active Listening: Children learn to pay attention to their peers, which helps them understand different perspectives and builds empathy.
- Conflict Resolution: Navigating disagreements with friends teaches children how to articulate their feelings and negotiate solutions.
- Non-Verbal Communication: Understanding body language and facial expressions is key to developing social awareness and responding appropriately in various situations.
- Self-Expression: Engaging in group discussions and cooperative play allows children to communicate their thoughts and feelings effectively.
Teaching emotional regulation is another vital component of social and emotional learning in early childhood education. By introducing techniques for managing emotions, educators equip young learners with the tools to handle challenges with more resilience. Techniques include:
Techniques for Teaching Emotional Regulation
Incorporating emotional regulation strategies into early childhood education can profoundly impact a child’s ability to manage their feelings. Techniques that can be implemented include:
- Mindfulness Activities: Simple breathing exercises or guided imagery help children learn to focus and calm their minds.
- Emotion Identification: Teaching children to identify and label their emotions fosters self-awareness and helps them understand their reactions.
- Role-Playing Scenarios: Engaging children in role-play situations allows them to practice coping strategies and responses to various emotional triggers.
- Storytelling: Sharing stories that revolve around emotions helps children relate to characters and understand complex feelings.
“Emotional regulation is a skill that can be taught and practiced, allowing children to thrive in the face of challenges.”
By embedding these techniques into the curriculum, educators can significantly enhance a child’s capacity for emotional regulation, leading to better social interactions and resilience in their future endeavors. This groundwork not only prepares children for academic success but also equips them with lifelong skills for personal growth and interpersonal relationships.
The Role of Play in Learning
Play is often seen as a simple pastime for children, but its role in early childhood education is far more profound. It serves as a fundamental learning tool that fosters a wide range of developmental skills. Through play, children engage with the world around them, exploring concepts of problem-solving, collaboration, and creativity. This active engagement not only enhances their cognitive abilities but also lays the groundwork for their future success in various aspects of life.
The significance of play as a learning tool cannot be overstated, as it provides a rich, interactive context for children to absorb knowledge and skills naturally and enjoyably.
Structured play activities specifically designed for educational purposes can enhance children’s learning experiences. These activities foster a playground of opportunities for acquiring essential skills across multiple domains, including cognitive, social, and emotional development. Here are some examples of play-based learning activities that promote various skills:
Examples of Play-Based Learning Activities
Play-based learning activities can be both fun and educational, allowing children to explore and learn in an engaging environment. These activities can promote different skills crucial for holistic development. Some notable examples include:
- Role-Playing: This encourages social skills and empathy as children take on different roles and perspectives, such as playing house or pretending to be community helpers.
- Building Blocks: Playing with blocks aids in fine motor skills, spatial awareness, and problem-solving as children create structures and navigate design challenges.
- Arts and Crafts: Engaging in creative activities like painting, drawing, or crafting helps develop fine motor skills, encourages self-expression, and fosters creativity.
- Outdoor Games: Games like tag or obstacle courses promote physical development, coordination, and teamwork.
- Puzzles and Board Games: These encourage critical thinking, strategy development, and turn-taking, enhancing cognitive skills and social interaction.
Structured play is not merely about allowing children to play freely; it involves creating an environment where play is guided to achieve specific learning outcomes. Such structured play can significantly lead to the enhancement of creative and critical thinking skills. By navigating challenges and making decisions during play, children learn to think outside the box and approach problems from different angles.
“Through play, children learn to engage with concepts in meaningful ways, enhancing their creativity and critical thinking.”
Providing opportunities for structured play allows educators to weave learning objectives into playful experiences, ensuring children are not only enjoying themselves but also developing essential skills that will support their lifelong journeys. Through the art of play, the foundation for future success is built, making it an indispensable aspect of early childhood education.
Parental Involvement and Support
Parental involvement plays a pivotal role in shaping the educational outcomes of young children. When parents actively engage in their child’s education, it can lead to improved academic performance, better social skills, and a more positive attitude toward learning. The connection between home and school is crucial; it creates a supportive environment where children feel encouraged to explore new concepts and ideas.The impact of parental engagement in early education is profound.
Research indicates that children whose parents are involved in their education tend to have higher grades, better test scores, and improved behavior in school settings. This engagement can manifest in various ways, from participating in school events to setting up a conducive learning environment at home. With this in mind, fostering strong partnerships between families and educators is essential for maximizing a child’s potential.
Strategies for Fostering Strong Partnerships
Creating a collaborative relationship between families and educators requires intentional efforts from both parties. Here are effective strategies to strengthen this partnership:
- Regular Communication: Establish open lines of communication through newsletters, emails, or parent-teacher conferences to keep parents informed about their child’s progress and school activities.
- Involvement Opportunities: Provide various ways for parents to participate, whether through volunteering, attending workshops, or being part of school committees.
- Shared Goals: Work together with parents to set educational goals for their children, ensuring everyone is on the same page regarding expectations and progress.
- Parent Education: Offer workshops that equip parents with tools and resources to support their child’s learning at home, covering topics like literacy, math skills, and social-emotional development.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Implement ways for parents to provide feedback about school programs, which encourages their active role in decision-making processes.
These strategies not only enhance parental engagement but also create a supportive community that values the contributions of both families and educators.
Guide for Parents to Support Learning at Home
Supporting a child’s learning at home is crucial for reinforcing concepts taught at school. Here is a guide to help parents effectively engage with their child’s educational journey:
1. Create a Routine
Establishing a consistent daily routine helps children understand the importance of time management and enhances their ability to focus on tasks.
2. Encourage Reading
Set aside time each day for reading together. This not only builds literacy skills but also strengthens the parent-child bond as they explore stories together.
3. Use Everyday Situations
Incorporate learning into daily activities. For instance, cooking can teach math through measuring ingredients, while shopping can enhance vocabulary and mathematical skills.
4. Foster Independence
Encourage children to take responsibility for their own learning by allowing them to choose activities or projects that interest them.
5. Celebrate Achievements
Recognize and celebrate both small and big accomplishments. This boosts a child’s self-esteem and motivates them to continue striving for success.
6. Limit Distractions
Designate a quiet, dedicated study space free from distractions, allowing the child to concentrate and engage with their learning materials effectively.
7. Communicate with Educators
Maintain ongoing dialogue with teachers to understand how to best support the learning objectives set in the classroom.
Parental involvement is the key to unlocking a child’s potential and fostering a love for lifelong learning.
Diverse Learning Environments
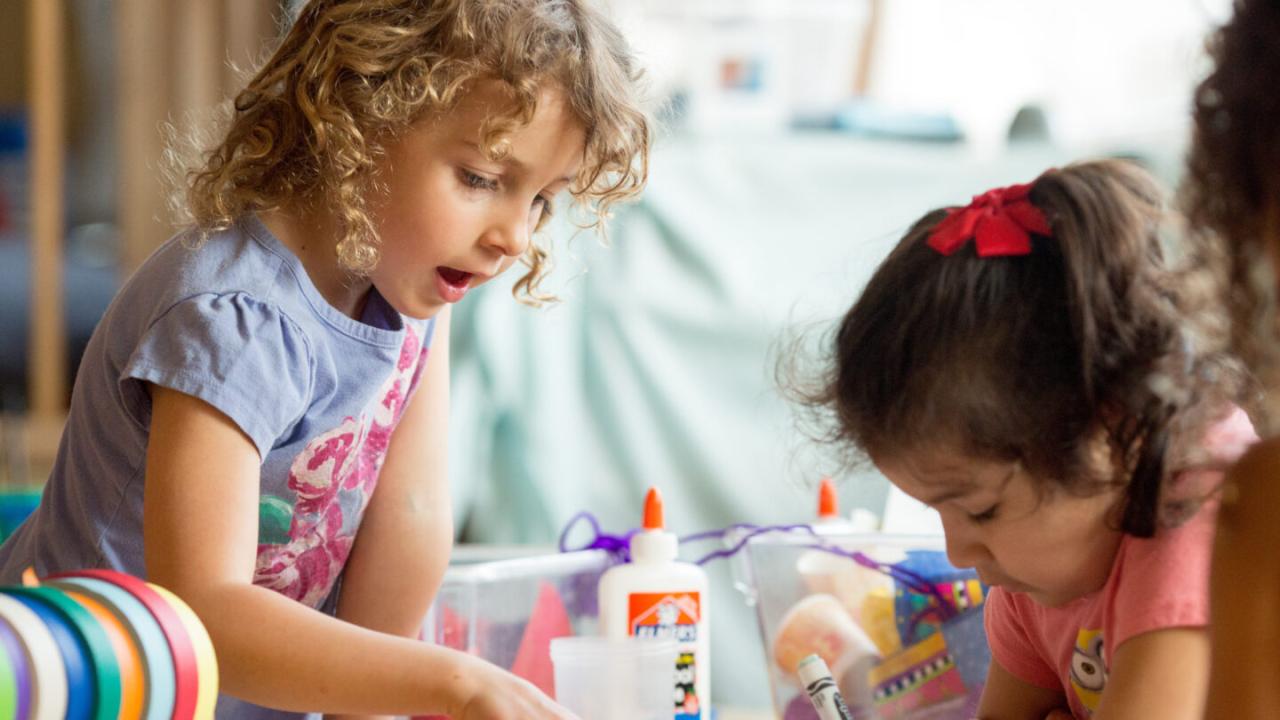

The value of diverse learning environments in early childhood education cannot be overstated. Inclusive educational settings foster a sense of belonging and acceptance among children from all backgrounds while promoting personal growth and community building. Such environments encourage children to interact with their peers, learn from one another, and embrace differences, ultimately shaping a more equitable society. Creating inclusive educational settings involves adapting early childhood education programs to cater to the diverse needs of children.
This adaptation ensures that every child, regardless of their background or abilities, receives equitable opportunities for learning and development. Educators play a crucial role in this process by implementing strategies that promote accessibility and inclusivity.
Strategies for Inclusive Education
There are various methods to adapt early childhood education programs to meet the diverse needs of children, including:
- Personalized Learning Plans: Developing individualized plans that Artikel specific goals and tailored strategies for each child ensures that their unique needs are acknowledged and addressed.
- Differentiated Instruction: Employing various teaching methods and materials allows educators to cater to different learning styles and abilities, ensuring that all children can engage with the curriculum.
- Universal Design for Learning (UDL): Implementing UDL principles encourages the creation of flexible learning environments that accommodate all learners by providing multiple means of engagement, representation, and action.
- Collaboration with Specialists: Partnering with special education professionals and other specialists helps educators better understand and meet the diverse needs of their students.
- Training and Professional Development: Ongoing training for educators focused on inclusive practices enhances their skills and knowledge, equipping them to foster a more inclusive learning environment.
Comparison of Educational Philosophies
Different educational philosophies offer distinct approaches to early childhood learning, significantly impacting how diverse learning environments are shaped. Comparing several philosophies can highlight their unique contributions:
| Educational Philosophy | Key Features |
|---|---|
| Montessori | Emphasizes child-led learning and exploration within a prepared environment that supports diverse needs and interests. |
| Reggio Emilia | Focuses on the child as an active participant in their learning, utilizing project-based approaches that incorporate community involvement and respect for diverse cultures. |
| Waldorf | Prioritizes creativity and imagination through arts-infused education, promoting social and emotional development within a nurturing environment. |
| HighScope | Encourages active participatory learning where children engage in their own learning experiences while fostering social interactions and relationships. |
Inclusive education settings play a critical role in shaping children’s future success. By embracing diverse learning environments and employing effective strategies, educators can provide valuable experiences that foster growth, understanding, and collaboration among young learners.
Early Intervention Programs
Early intervention programs are crucial for at-risk children, providing them with the support needed to thrive both academically and socially. These programs aim to identify challenges early on, allowing for timely assistance that can significantly alter a child’s developmental trajectory. By implementing effective strategies that address the unique needs of these children, we can help them achieve better outcomes in their education and overall life.Effective early intervention strategies are characterized by several key elements.
First, they are individualized, meaning they cater specifically to the unique needs of each child. Additionally, these programs are evidence-based, utilizing research-backed methods that have been shown to be successful. Collaboration with families is another essential characteristic, as parental involvement enhances the effectiveness of the interventions. Lastly, continuous monitoring and assessment are important to adapt strategies as the child’s needs evolve over time.
Role of Assessments in Early Intervention
Assessments play a vital role in identifying children who may benefit from early intervention services. By evaluating cognitive, social, and emotional development, professionals can pinpoint areas where a child may be struggling. These assessments can include standardized tests, observational methods, and interviews with parents and caregivers. Early identification through assessments allows for quicker intervention, which can lead to more favorable outcomes for the child.One effective approach is to use a multi-tiered system of support (MTSS), which provides a framework for assessing and addressing the needs of students at various levels of risk.
This system helps to ensure that children receive appropriate interventions based on their specific challenges and strengths.
Resources for Early Intervention Services
For families seeking early intervention services, a variety of resources are available to help navigate the process. These resources offer support in identifying services, accessing funding, and understanding the rights of children with developmental delays. Below is a table outlining some key resources:
| Resource | Description | Contact Information |
|---|---|---|
| Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) | A federal law ensuring services to children with disabilities. | www.idea.ed.gov |
| Zero to Three | A national organization focused on the development of infants and toddlers. | www.zerotothree.org |
| Local Early Intervention Programs | State-specific programs offering assessments and resources for families. | Check local government websites for contact information. |
| Parent Training and Information Centers (PTIs) | Offer resources and support for parents of children with disabilities. | www.parentcenterhub.org |
The Long-term Benefits of Early Education
Investing in early childhood education yields substantial benefits that extend far beyond the classroom. Statistical evidence highlights a clear correlation between early education and later academic success, illustrating the critical importance of these formative years. The economic advantages of such investments also resonate throughout society, reinforcing the argument for prioritizing early education initiatives.
Correlation Between Early Education and Academic Success
Research consistently shows that children who participate in high-quality early childhood education programs tend to perform better academically in later years compared to their peers who do not have such experiences. A seminal study by the National Center for Children in Poverty found that children enrolled in early education programs are 40% more likely to graduate high school. Furthermore, a report from the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) indicates that for every dollar invested in early childhood education, there can be a return of up to $7 in terms of improved educational outcomes and reduced societal costs related to crime and welfare.
Economic Impacts of Investing in Early Education
Investing in early education not only benefits children but also has a profound economic impact on society as a whole. The costs associated with inadequate early education manifest in higher rates of remedial education, increased healthcare needs, and elevated crime rates. According to a study by the Heckman Equation, each dollar spent on early childhood education yields an ROI that can exceed $13, demonstrating the long-term fiscal advantages for taxpayers and governments alike.
Case Studies Highlighting Success Stories, How Early Childhood Education Shapes Future Success
Numerous case studies illustrate the transformative effects of early childhood education programs. For instance, the Perry Preschool Project, which targeted disadvantaged children in Michigan, reported that participants had significantly higher earnings and lower rates of criminal activity in adulthood compared to non-participants. Additionally, the High/Scope Educational Research Foundation’s study indicated that children enrolled in the High/Scope preschool program were more likely to pursue higher education and secure stable employment later in life.
“High-quality early childhood education is not just a benefit for the individual child; it is an investment in the future of our society.”
Such examples showcase the potential for early education to alter life trajectories, underscoring the necessity for broad community and governmental support for these programs. By prioritizing early education, society not only fosters individual success but also cultivates a more educated and productive population overall.